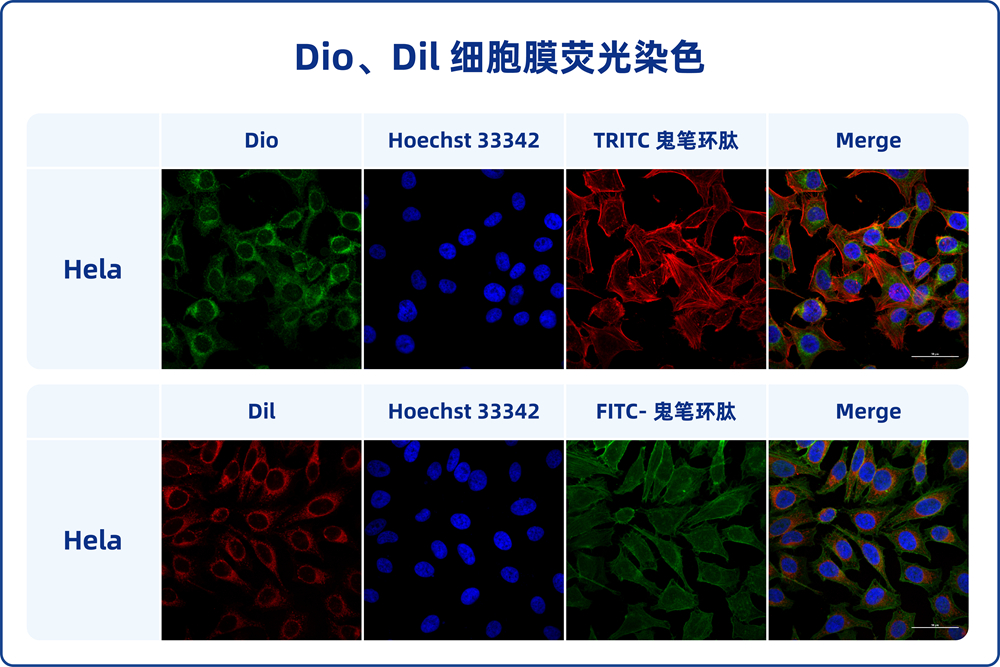
Description
Product Information
Product Name: DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescence Staining Kit
Product Description
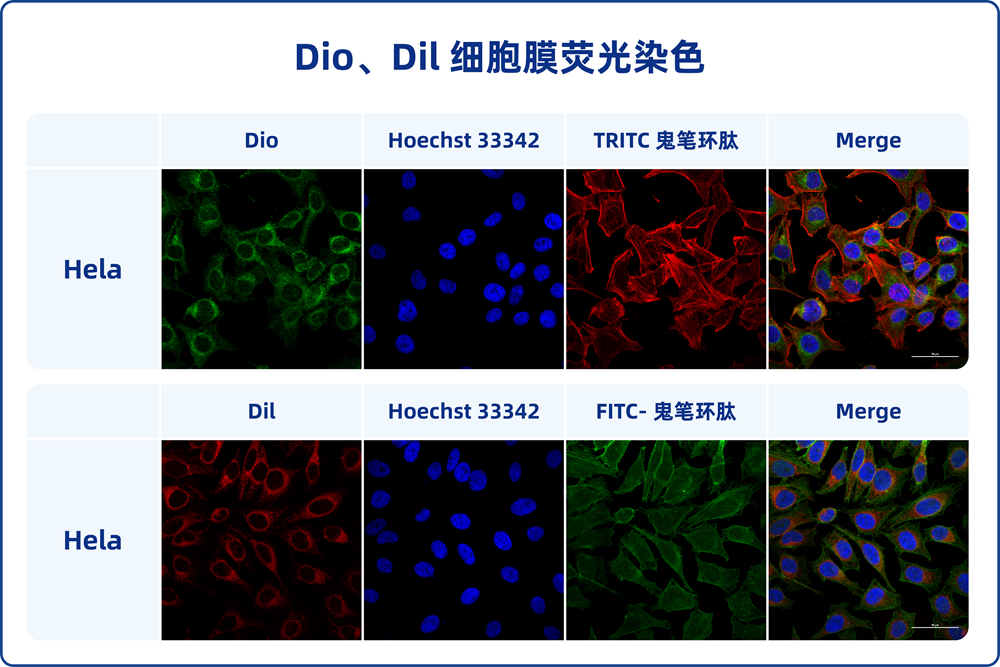
The DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescence Staining Kit is designed for staining cell membranes with a green fluorescent dye called DiO (3,3′-Dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine Perchlorate). DiO is a lipophilic dye that selectively incorporates into cell membranes, making it an excellent tool for labeling and visualizing cell membranes under fluorescent microscopy.
This staining kit provides a simple and effective way to label cell membranes with green fluorescence. The DiO dye is incorporated into the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, resulting in a strong and stable fluorescent signal that outlines the cell’s outer boundary. This allows researchers to study cell morphology, interactions, and migration patterns.
The kit includes all the necessary components for the staining procedure, including the DiO dye, staining buffer, and detailed instructions. The staining process involves a few simple steps and can be completed within a short period of time.
Storage and Transportation
Store the kit components according to the provided instructions. Proper storage conditions ensure the stability and effectiveness of the staining reagents. The shelf life of the kit is indicated in the product documentation.
Usage
The DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescence Staining Kit is intended for research purposes and is not suitable for clinical diagnosis or therapeutic applications.
Please refer to the provided instructions for detailed information on how to use the kit and perform the cell membrane staining procedure.
Product Information
Product Name: DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescence Staining Kit
Product Number: G1704
Specification: 100-1000 tests
Product Description
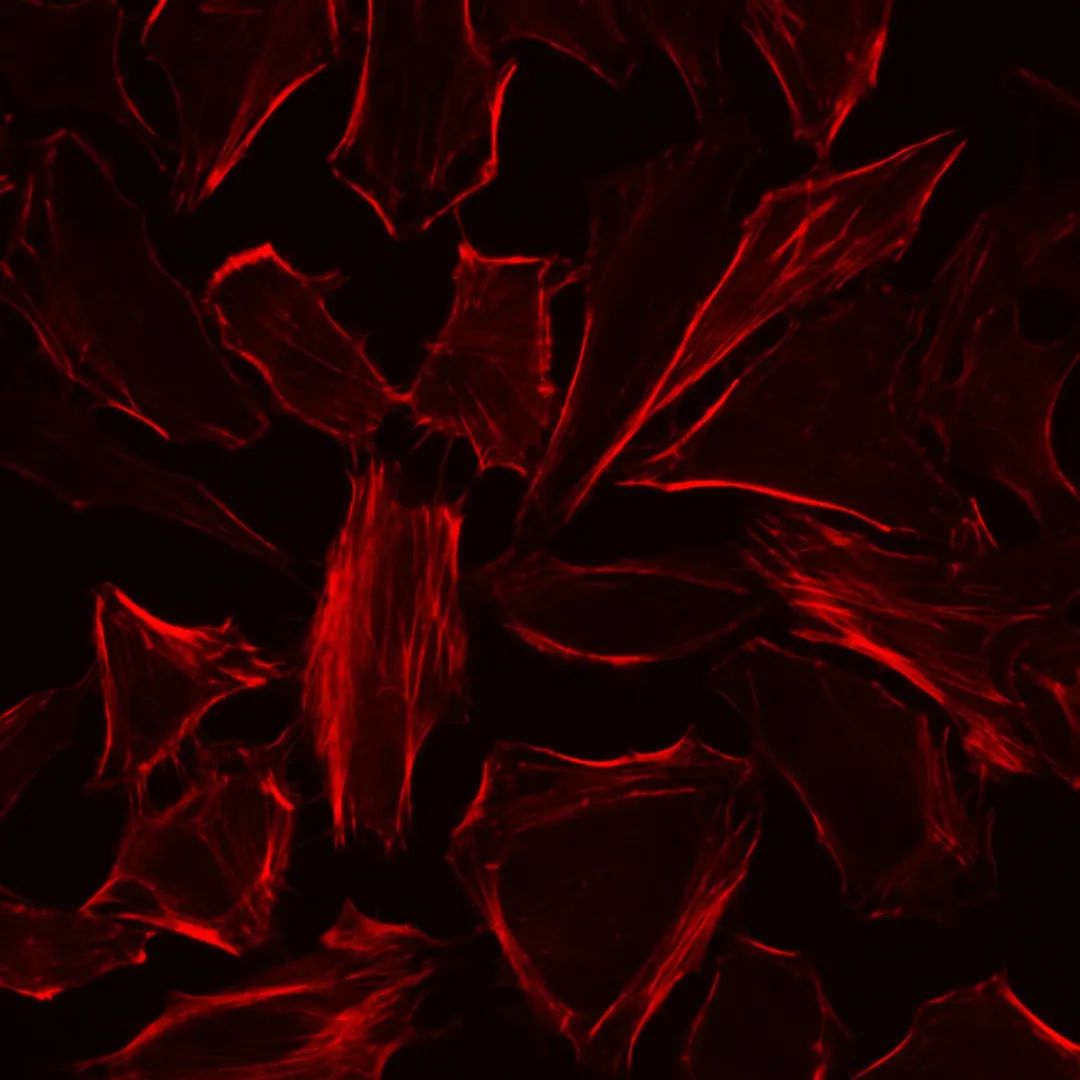
DiO, also known as DiOC18(3), whose full Chinese name is 3-octadecyl-2-[3-(3-octadecyl-2(3H)-benzoxazol-2-ylidene)-1-propenyl]benzoxazolium perchlorate, with a molecular weight of 881.72, is a lipophilic long-chain dialkylcarbocyanine fluorescent dye. It is commonly used for labeling cell membranes and other lipophilic biological structures. DiO enters the cell membrane and gradually diffuses laterally, resulting in staining of the entire cell membrane. The fluorescence of DiO is weak before entering the cell membrane, but its intensity significantly increases upon binding to cells, emitting green fluorescence when excited, which can be detected using standard FITC filter settings. DiO’s maximum excitation wavelength is 484 nm, and its maximum emission wavelength is 501 nm. Based on its characteristics, DiO can be used for staining live cells, fixed cells, tissues, or sections. Additionally, DiO probes generally do not affect cell viability, making it suitable for labeling cells or substances (such as exosomes) for tracing and detection.
The DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescence Staining Kit includes DiO fluorescent probe and optimized staining buffer, which makes cell membrane staining faster, fluorescence brighter and more stable, and overall results better.
Storage and Transportation
Transport on dry ice (wet ice) and store at -20°C in the dark. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. The shelf life is at least 6 months.
Components of the Kit
Component Number
Component
G1704
G1704-1
DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescent Probe
400 μL
G1704-2
Staining Buffer
100 mL
Instruction Manual
1 copy
Operating Instructions
- Preparation of DiO Staining Solution:
1.1. Mix the DiO Cell Membrane Green Fluorescent Probe with the staining buffer in a 1:250 ratio to prepare the DiO staining solution (prepare and use immediately). Note that the dilution ratio of the DiO probe can be adjusted between 1:250 to 1:500 depending on the specific situation to achieve the best staining effect.
- Staining of Suspended Live Cells:
2.1. Collect suspended cells, centrifuge at 500-1000 g for 3-5 minutes at room temperature, and remove the cell supernatant.
2.2. Resuspend cells using the DiO staining solution to achieve a cell density of 1-2×106 cells/mL.
2.3. Incubate at 37°C in the dark for 5-20 minutes. Adjust the staining time based on cell type to achieve optimal staining results.
2.4. Centrifuge at 500-1000 g for 3-5 minutes at room temperature, and remove the DiO staining solution.
2.5. Wash cells with pre-warmed PBS or cell culture medium at 37°C, centrifuge at 500-1000 g for 3-5 minutes, and remove the supernatant.
2.6. Repeat step 2.5 once.
2.7. Analyze with a flow cytometer or transfer cells to a multi-well plate, cell culture dish, or glass slide for observation under a fluorescence microscope. DiO’s maximum excitation wavelength is 484 nm, and its maximum emission wavelength is 501 nm.
- Staining of Adherent Live Cells (using a 6-well plate as an example):
3.1. Pre-plate cells at a certain density in a 6-well plate.
3.2. Remove the cell culture medium and wash cells twice with PBS (G4202). Add 1 mL of DiO staining solution (adjust for different plate formats to ensure cell coverage).
3.3. Incubate at 37°C in the dark for 5-20 minutes. Adjust the staining time based on cell type to achieve optimal staining results.
3.4. Remove the DiO staining solution. Wash cells 1-2 times with pre-warmed PBS.
3.5. Add pre-warmed PBS or cell culture medium at 37°C and observe under a fluorescence microscope. DiO’s maximum excitation wavelength is 484 nm, and its maximum emission wavelength is 501 nm.
- Staining of Fixed Adherent Cells or Tissue Sections:
4.1. Pre-treatment of Samples:
For cells: Remove the cell culture medium, wash with PBS 1-2 times, fix with 4% paraformaldehyde fixative solution (G1101) at room temperature for 10 minutes. Remove the fixative, wash with PBS 2-3 times.
For tissue sections, dewax paraffin sections in water; for frozen sections, thaw and wash.
4.2. Treat cells or sections with 0.1-0.5% Triton-100 (prepared in PBS) for 10 minutes at room temperature. Remove the permeabilization solution and wash with PBS 2-3 times.
4.3. (Optional, immunofluorescence labeling) Incubate with antibodies or other dyes according to the immunofluorescence staining method. Note: Blocking solution, antibody dilution, and washing solutions during antibody incubation should not contain detergents.
4.4. Add an appropriate volume of DiO staining solution to cover cells or tissue sections. Incubate at 37°C in the dark for 5-20 minutes. Adjust the staining time based on cell or tissue samples to achieve optimal staining results.
4.5. Wash cells or sections with PBS 2-3 times and observe under a fluorescence microscope. (For cells, cover with an appropriate volume of PBS). DiO’s maximum excitation wavelength is 484 nm, and its maximum emission wavelength is 501 nm.
- Exosome Fluorescent Labeling:
5.1. Re-suspend the extracted exosome precipitate in an appropriate volume of DiO staining solution.
5.2. Incubate the sample at 37°C in the dark for 30 minutes.
5.3. Dilute the sample with 10 times the volume of PBS (optional).
5.4. Repeat the previous exosome extraction process to remove excess dye.
5.5. Collect the exosome precipitate, re-suspend in PBS, and obtain DiO-labeled exosomes. These can be used for subsequent experiments, such as cell uptake.
Precautions
- Fluorescent dyes may undergo quenching, so avoid light exposure to slow down fluorescence quenching.
- Due to the lipophilic nature of the probe, avoid using reagents containing glycerol or other organic compounds during the experiment, as they may affect the staining effect.
- When fixation is required, fix samples in 4% paraformaldehyde; using inappropriate fixatives may lead to high fluorescence background.
- Optimal dilution ratio and incubation time of the probe should be adjusted appropriately based on the sensitivity of cells and the experimental purpose.
- For your health and safety, please wear lab coats and gloves while operating.
This product is for research purposes only and is not intended for clinical diagnosis.
Please note that this translation may not capture all nuances of the original text, and it’s always a good practice to refer to the original documentation for accurate information.