Description
Product Description:
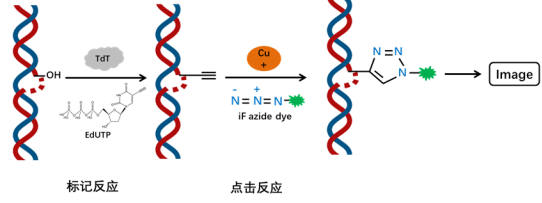
The fragmentation of chromosomal DNA during cell apoptosis is a progressive and staged process. Initially, chromosomal DNA is degraded into large fragments of 50-300 kb by endogenous nucleases. Then, approximately 30% of the chromosomal DNA undergoes random cleavage between nucleosome units mediated by Ca2+ and Mg2+-dependent endonucleases, resulting in the formation of 180-200 bp nucleosomal DNA fragments. Therefore, in the late stage of cell apoptosis, DNA is degraded into fragments of 180-200 bp, exposing a large number of 3′-OH ends on the fragmented genomic DNA. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) is a template-independent DNA polymerase that catalyzes the addition of deoxynucleotides to the 3′-OH ends of fragmented DNA molecules. Thus, the TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling) assay kit can be used to detect DNA fragmentation in the nuclei of tissue cells during the late stage of apoptosis.
The principle of this assay is that under the action of TdT enzyme, the exposed 3′-OH ends of the genomic DNA during DNA fragmentation are labeled with EdUTP (a dUTP modified with an alkyne group). The alkyne group undergoes a click reaction with an azide dye catalyzed by monovalent copper ions, resulting in the site-specific incorporation of a fluorescent group. The kit utilizes iF647 azide as the fluorescent dye, which can be detected using a fluorescence microscope or flow cytometer (excitation at 656 nm, emission at 670 nm). Compared to other modified dUTPs, EdUTP has smaller steric hindrance and is more easily incorporated into DNA ends by TdT enzyme.
This assay kit has a wide range of applications and is suitable for the detection of cell apoptosis in paraffin tissue sections, frozen tissue sections, cell smears, and cell suspensions.
Please note that it’s important to follow the instructions and protocols provided with the assay kit for accurate and reliable results.
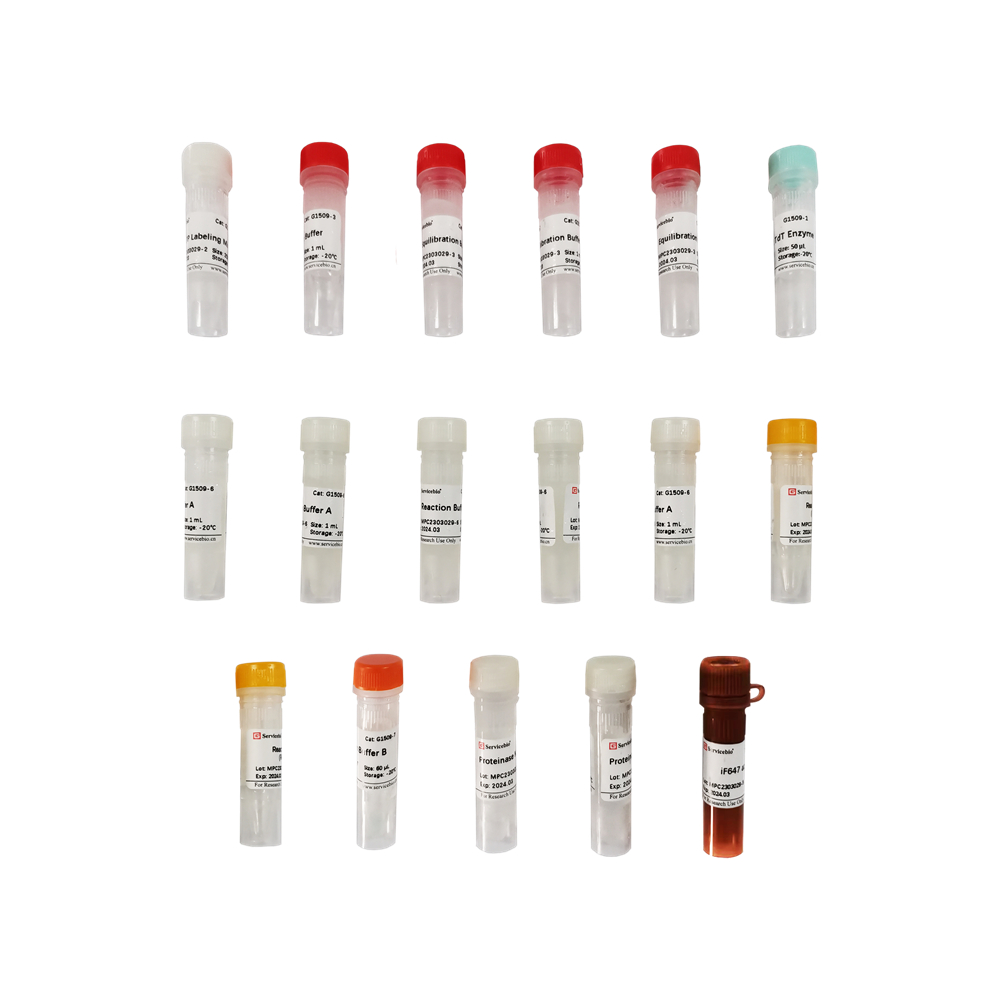
| Component Number | Component | G1504-50T |
| G1509-1 | Recombinant TdT Enzyme | 50 µL |
| G1509-2 | EdUTP Labeling Mix | 250 µL |
| G1509-3 | Equilibration Buffer | 5×1 mL |
| G1509-4 | Proteinase K(200 µg/mL) | 1 mL |
| G1509-5 | iF647 azide dye | 80 μL |
| G1509-6 | Reaction Buffer A | 5×1 mL |
| G1509-7 | Reaction Buffer B | 60 μL |
| G1509-8 | Reaction additive(Reagent C) | 2×100 mg |
| Instruction | 1 | |
Preparations before the Experiment:
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (recommended: G0002 or G4202).
- Fixative solution: 4% paraformaldehyde dissolved in PBS, pH 7.4 (recommended: G1101).
- Permeabilization solution: 0.1% Triton X-100 dissolved in 0.1% sodium citrate (recommended: G1204).
- 0.2% Triton X-100 in PBS; 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS containing 5 mg/mL BSA.
- If nuclear staining is required, prepare DAPI (2 µg/mL), Hoechst 33258, or PI (1 µg/mL) (recommended: G1012, G1011, G1021).
- If a positive control experiment is needed, prepare DNase I (recommended: G3342).
- If using a flow cytometer, prepare PI staining solution (recommended: G1021) and RNase A (DNase free) (recommended: G3413).
- Reaction additive (Reagent C): Dissolve 100 mg of powder in 1 mL of ultrapure water (ready for use). Aliquot 100 μL and store at -20°C, and keep the remaining powder as a backup. (Reagent C is prone to oxidation, so it is recommended to avoid prolonged exposure to air. After preparing the aqueous solution, it is strongly advised to aliquot and use small portions. A slight color change in the Reagent C solution does not affect the TUNEL reaction system. If it turns brown, it indicates that the component has expired.)
- If the background color of the results is too dark, it may be due to insufficient washing during the experiment or residual fixative solution.
- Pay attention to the order and sequential addition of the components in the TUNEL reaction system. Mix while adding.
- For your safety and health, wear lab coats and disposable gloves during the operation.
Note: It is important to follow the specific instructions provided with the TUNEL assay kit for proper usage and interpretation of the results.
Operating steps:
- Sample preparation
A. Paraffin-embedded tissue sections
- Soak the paraffin tissue sections in xylene at room temperature for 5-10 minutes, repeat 2-3 times. Then immerse them in absolute ethanol without water for 5 minutes, repeat 2 times. Finally, immerse them in gradient ethanol (85%, 75%, double-distilled water) once each for 5 minutes.
- Gently rinse the sections with PBS and remove excess liquid around the samples. Use a histology pen to draw a small circle approximately 2-3 mm away from the tissue perimeter. This is to facilitate subsequent permeabilization treatment and balanced labeling. Throughout the experiment, make sure not to let the samples dry. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
- Prepare Proteinase K working solution: Dilute Proteinase K (200 µg/mL) stock solution with PBS in a 1:9 ratio to obtain a final concentration of 20 μg/mL.
- Add 100 μL of the Proteinase K working solution to each sample, ensuring complete coverage. Incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes.
(Note: Proteinase K treatment helps the staining reagents penetrate the tissue and cells in subsequent steps. Both over- and under-incubation can affect labeling efficiency. To obtain better results, optimize the incubation time according to the specific conditions.)
- Rinse the samples with PBS solution three times for 5 minutes each (Proteinase K should be thoroughly washed away to avoid interference with subsequent labeling reactions). Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
- (Optional step) Remove excess liquid from the samples and add an appropriate amount of membrane-breaking solution to infiltrate the tissue. Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. After membrane-breaking treatment, rinse the samples with PBS solution three times for 5 minutes each. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
B. Frozen tissue sections
- Immerse the tissue sections in a fixative solution and incubate at room temperature for 10-15 minutes.
- Remove the tissue sections from the fixative solution and allow them to air dry in a fume hood.
- Rinse the tissue sections in distilled water or PBS to remove residual fixative.
- Use a histology pen to draw a small circle approximately 2-3 mm away from the tissue perimeter. This is to facilitate subsequent permeabilization treatment and balanced labeling. Throughout the experiment, make sure not to let the samples dry. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
- Prepare Proteinase K working solution: Dilute Proteinase K (200 µg/mL) stock solution with PBS in a 1:9 ratio to obtain a final concentration of 20 μg/mL.
- Add 100 μL of the Proteinase K working solution to each sample, ensuring complete coverage. Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes.
(Note: Proteinase K treatment helps the staining reagents penetrate the tissue and cells in subsequent steps. Both over- and under-incubation can affect labeling efficiency. To obtain better results, optimize the incubation time according to the specific conditions.)
- Rinse the samples with PBS solution 2-3 times to remove excess liquid (Proteinase K should be thoroughly washed away to avoid interference with subsequent labeling reactions). Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
- (Optional step) Add an appropriate amount of membrane-breaking solution to the tissue, fully infiltrating the tissue. Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. After membrane-breaking treatment, rinse the samples with PBS solution to remove excess liquid. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
C. Cell Crawling Assay
- Cultivate adherent cells on Lab-Tek chamber slides. After inducing apoptosis, gently rinse the chamber slides twice with PBS.
- Add an appropriate amount of fixative solution to cover the tissue in each chamber slide. Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes.
- Remove the fixative solution and wash the samples three times with PBS for 5 minutes each.
- Immerse each sample in a 0.2% Triton X-100 solution prepared in PBS for permeabilization at room temperature for 5 minutes.
- Immerse and wash the samples 2-3 times in an open beaker containing PBS solution.
- Carefully remove excess liquid and use filter paper to gently dry the liquid around the samples on the chamber slides. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.D. Cell Smear
- Resuspend cells in PBS at a concentration of approximately 2×107 cells/mL. Pipette 50-100 μL of cell suspension onto a frosted glass slide, and gently spread the cell suspension using a clean coverslip.
- Immerse the cell smear in a staining dish containing fixative solution to fix the cells. Place it at 4°C for 25 minutes.
- Dip the slide into PBS and let it sit at room temperature for 5 minutes. Repeat this step once.
- Carefully remove excess liquid and use filter paper to gently dry the excess liquid around the sample on the slide. Use a histology pen to draw a small circle along the outer contour of the cells. This will facilitate downstream permeabilization and labeling procedures. Make sure to prevent the sample from drying during the experiment.
- Immerse each sample in a 0.2% Triton X-100 solution prepared in PBS at room temperature for 5 minutes for permeabilization.
- Immerse and wash the samples 2-3 times in an open beaker containing PBS solution.
- Gently remove excess liquid and use filter paper to carefully dry the liquid around the sample on the slide. Place the processed samples in a humid box to keep them moist.
II. DNase I Treatment Positive Control Experiment (Optional Steps)
After permeabilizing the samples, DNase I treatment can be performed to prepare the positive control.
- Add 100 μL of 1× DNase I Buffer (prepare by taking 10 μL of 10× DNase I Buffer and adding 90 μL of deionized water) to the permeabilized sample. Incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes.
- Gently remove excess liquid and add 100 μL of working solution containing DNase I (20 U/mL) to the sample (prepare by taking 10 μL of 10× DNase I Buffer, adding 2 μL of DNase I, and then adding 88 μL of deionized water). Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Gently remove excess liquid and thoroughly wash the slides in a staining dish containing PBS, repeating the washing step 3-4 times.
(Note: The positive control slides must be placed in a separate staining dish. Otherwise, residual DNase I on the positive control slides may introduce high background to the experimental slides.)
III. Labeling and Detection
- Equilibration: Add 50 μL of Equilibration Buffer to each sample, ensuring coverage of the entire area of interest. Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Labeling solution preparation: Thaw the EdUTP Labeling Mix and Equilibration Buffer on ice. Mix Recombinant TdT enzyme, EdUTP Labeling Mix, and Equilibration Buffer in a ratio of 1 μL:5 μL:50 μL (1:5:50) to prepare enough TdT incubation buffer for all experiments. Adjust the volumes of the reagents used in the experiment accordingly, proportionally to the size of the slides.
- Negative control system: Prepare a control TdT incubation buffer without Recombinant TdT enzyme, replacing it with ddH2O.
- Labeling: Remove the Equilibration Buffer as much as possible, then add 56 μL of TdT incubation buffer to each tissue sample. Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour, making sure the slides do not dry.
- Immediately wash the tissue samples with PBS, performing 4 washes of 5 minutes each.
- Click reaction: Remove the previous PBS buffer and add 100 μL of click reaction solution to each sample, ensuring complete coverage of the samples. Incubate at room temperature, protected from light, for 30 minutes. (Refer to the table below for the click reaction solution system. Add each reagent in the order listed while mixing. The proportions can be adjusted proportionally or decreased as needed. It is recommended to prepare the solution in advance.)
Note: The translation provided above is a direct translation of the given instructions. Some technical terms or details may require further clarification or context for complete understanding.
| Component | Volume |
| Reaction Buffer A | 925 μL |
| Reaction Buffer B | 10 μL |
| iF647 azide dye | 15 μL |
| Reaction additive(Reagent C) | 50 μL |
| total | 1000 μL |
- Remove the click reaction solution and immediately wash the samples with PBS buffer, performing 2-3 washes of 5 minutes each.
- Gently remove the PBS solution around the samples using a filter paper.
- Nuclear staining: Stain the samples in a staining dish by immersing the slides in a DAPI solution (prepared fresh and diluted with PBS) in a dark room. Incubate at room temperature for 8 minutes (or use Hoechst 33258 for nuclear staining).
- Mounting: After completing the sample staining, wash the tissue samples with PBS three times for 5 minutes each. Then gently remove excess liquid and apply anti-fade mounting medium (recommended: G1401) to mount the slides.
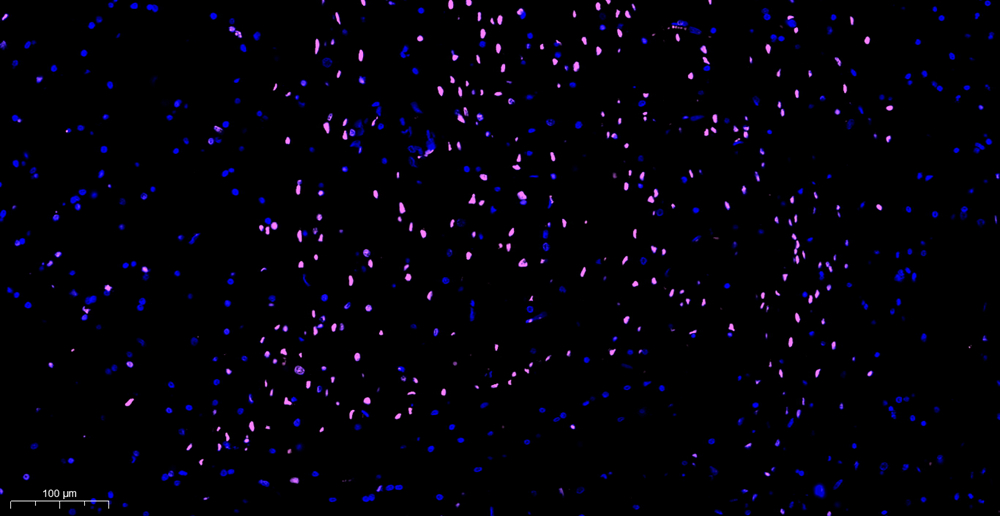
- Microscopic examination: Immediately analyze the samples under a fluorescence microscope. Handle the slides in a light-protected manner. DAPI will stain both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cells blue, while the iF647 azide dye incorporated in the apoptotic cell nuclei will exhibit pink fluorescence.
IV. Detection of Suspended Cells using Flow Cytometry
- Wash the cells to be analyzed twice with PBS, then centrifuge at 4°C (500 g) and resuspend in 500 µL of PBS.
- Fixation: Add 5 mL of 1% paraformaldehyde solution prepared in PBS to the samples to fix the cells. Place on ice for 20 minutes.
- Centrifuge the cells at 4°C, 300 g for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells twice in 5 mL of PBS. Finally, resuspend the cells in 500 µL of PBS.
- Permeabilization: Add PBS containing 0.2% Triton X-100 to the cell samples for permeabilization. Incubate at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to permeabilize the cells.
- Centrifuge the cells at 300 g for 10 minutes, resuspend in 5 mL of PBS, and repeat the centrifugation step. Then, resuspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS.
- Equilibration: Transfer approximately 2×106 cells to a microcentrifuge tube with a volume of 1.5 mL. Centrifuge at 300 g for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend in 80 μL of Equilibration Buffer. Incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes.
- Labeling solution preparation: Thaw the EdUTP Labeling Mix and Equilibration Buffer on ice. Mix Recombinant TdT enzyme, EdUTP Labeling Mix, and Equilibration Buffer in a ratio of 1 μL:5 μL:50 μL (1:5:50) to prepare enough TdT incubation buffer for all experiments and optional positive control reactions.
- Labeling: Centrifuge the cells at 300 g for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet in 56 μL of TdT incubation buffer. Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour, protected from light. Gently resuspend the cells every 15 minutes using a micropipette.
- After the reaction is complete, remove the labeling reaction solution and wash the samples with PBS, performing 3-4 washes of 5 minutes each.
- Click reaction: Remove the previous PBS buffer and add 100 μL of click reaction solution to each sample, ensuring complete coverage of the samples. Incubate at room temperature, protected from light, for 30 minutes. (Refer to the table below for the click reaction solution system. Add each reagent in the order listed while mixing. The proportions can be adjusted proportionally or decreased as needed. It is recommended to prepare the solution in advance.)
- Remove the click reaction solution, immediately wash the samples with PBS buffer, performing 2-3 washes of 5 minutes each.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100, with 5 mg/mL BSA. Wash the cells twice.
- Nuclear staining: Centrifuge at 300 g for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells in 0.5 mL of DAPI solution containing 250 μg of RNase A without DNAase. Incubate the cells in the dark at room temperature for 30 minutes (or use Hoechst 33258 for nuclear staining).
- Analyze the cells using a flow cytometer. DAPI will stain both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cells blue, while the iF647 azide dye incorporated in the apoptotic cell nuclei will exhibit green fluorescence.
more details please send Email. Thanks