Description
Product Introduction
Cell proliferation analysis is a common and important evaluation method in the field of life sciences, used to assess the impact of genes, drugs, and other factors on cells cultured in vitro, as well as to analyze the growth and renewal capacity of cells in different states or under various stimuli. Currently, there are various methods available for detecting cell proliferation, most of which rely on the measurement of metabolic enzymes produced by cells to indirectly assess cell proliferation activity (such as CCK-8 assay, MTT assay, etc.). However, factors such as drug effects and cell status can influence the results of these indirect methods. Directly detecting DNA synthesis in cells is recognized as the most accurate and effective method for assessing cell proliferation. However, both the originally used radiolabeling nucleoside incorporation method and the subsequent antibody-based BrdU method have their limitations.
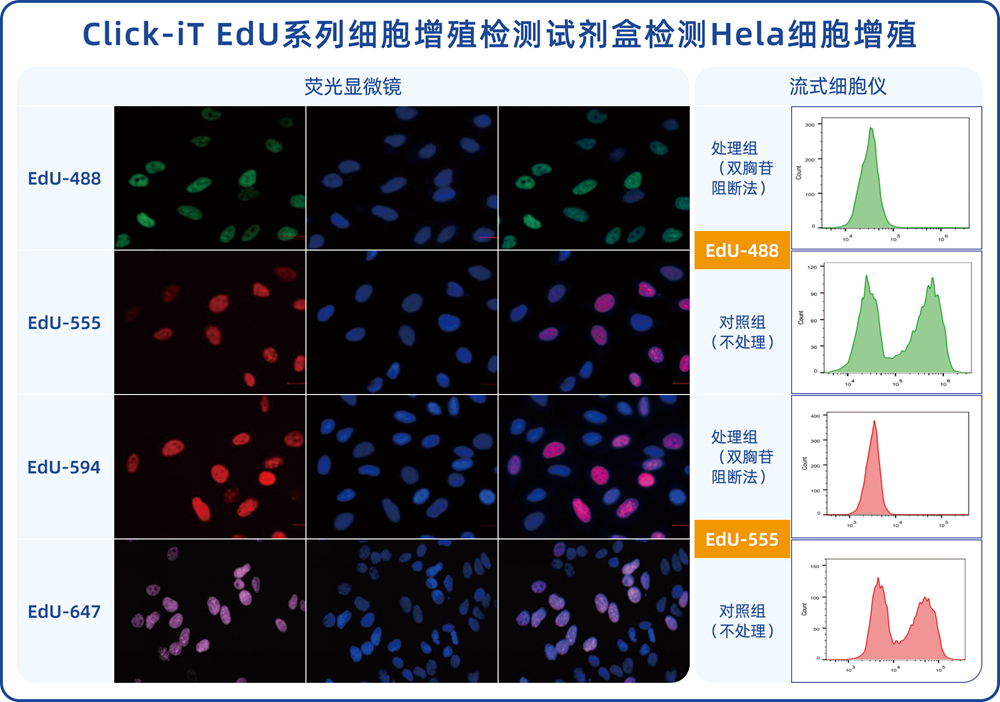
EdU (5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) is a thymidine analog containing an ethynyl group. When injected into animals or incubated with cells cultured in vitro, these small molecules can quickly diffuse into various organs and tissues and penetrate into cells. During the DNA synthesis phase of cell proliferation, EdU can replace thymidine (T) and be incorporated into newly synthesized DNA. The ethynyl group in the EdU molecule can undergo a “click” reaction with a fluorescent-labeled azide probe catalyzed by copper ions, forming a stable triazole ring, thereby allowing newly synthesized DNA to be labeled by the corresponding fluorescent probe. Compared to radiolabeling nucleoside incorporation methods, the EdU detection method does not have limitations such as radioactive contamination. Compared to the BrdU detection method, the EdU detection method does not require DNA denaturation treatment or antigen-antibody reactions, greatly reducing the complexity and time required for the experiment and making it more efficient, sensitive, stable, and accurate. This assay kit is designed for detecting cell proliferation in cells cultured in vitro or animal tissues. The fluorescent probe in this kit emits a pink (far-red) fluorescence, with a maximum excitation wavelength at 656 nm and a maximum emission wavelength at 670 nm. After labeling proliferating cells, the cell nuclei will exhibit bright pink fluorescence. Cell proliferation can be directly observed using fluorescence microscopy, laser confocal microscopy, or similar instruments in conjunction with a conventional cell nuclear stain (Hoechst 33342 nuclear stain provided in this kit). The fluorescence intensity of cell populations in vitro can also be measured using flow cytometry, allowing for the assessment of DNA replication activity during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Storage and Transportation
Transport on wet ice; store at -20°C, protected from light. EdU catalytic reagent (Component A) and reaction buffer can be stored at 4°C. Shelf life is 12 months.
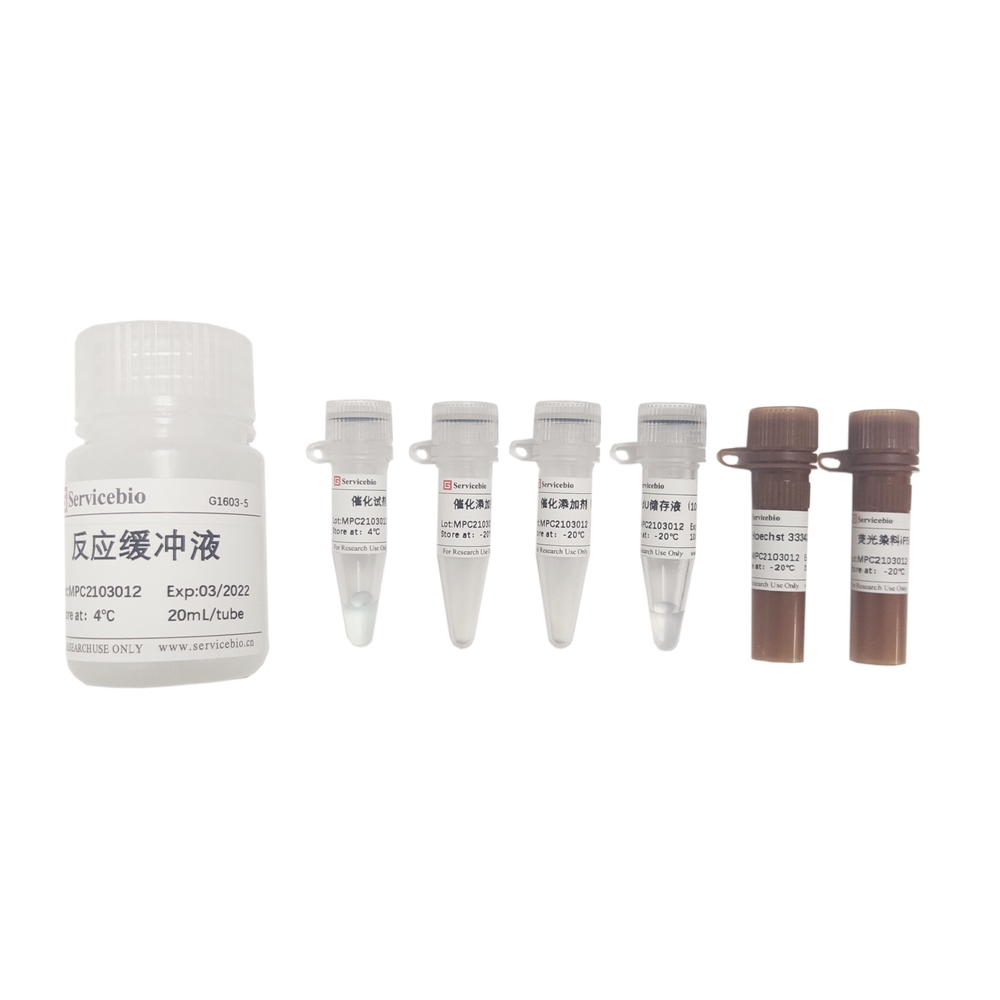
Composition
| Component Number | Component |
|---|---|
| G1604-100T | EdU Storage Solution (10 mM) |
| G1604-1 | 100 μL |
| G1604-2 | Catalytic Reagent (Component A) |
| G1604-3 | Fluorescent Dye iF647 (Component B) |
| G1604-4 | Catalytic Additive (Component C) – 2×100 mg (powder) |
| G1604-5 | Reaction Buffer – 20 mL |
| G1604-6 | Hoechst 33342 Staining Solution – 30 μL |
| Product Manual | 1 copy |
Note: The above reaction quantities are for 96-well plate detection.
Experimental Preparation
- Cell culture medium containing serum.
- Permeabilization solution: Buffer containing 0.2-0.5% Triton X-100 (recommended G1204).
- Fixative solution: 4% paraformaldehyde (recommended G1101) or similar reagents for fixation.
- PBS buffer (recommended G4202).
- Ultra-pure water.
- Reagents related to animal modeling and tissue sectioning (for animal tissue cell proliferation detection).
Procedure
- Preparation of cell samples and reagents:
1.1. Uniformly seed cells in a cell culture plate at a certain density (the seeding density depends on factors such as cell size and growth rate). After the cells adhere to the plate or reach a normal state, perform the corresponding drug stimulation or other treatments (for suspension cells, follow the standard procedures for suspension cells, including centrifugation steps for the overall experiment).
1.2. Centrifuge the catalytic additive (Component C), take 100 mg and dissolve it in 1 mL of ultra-pure water. Store the solution in aliquots at -20°C, and keep the remaining powder as a backup.
- Cell EdU labeling, fixation, and permeabilization:
2.1. Prepare 2×EdU incubation working solution: Add 2 μL of EdU storage solution (10 mM) to 1 mL of complete cell culture medium, resulting in a 20 μM 2×EdU incubation working solution. Preheat the solution in an incubator (preliminary experiments are recommended to explore the optimal EdU working concentration using 10 μM).
2.2. Remove half of the original cell culture medium from the culture plate using a medium exchange method, and replace it with an equal volume of preheated 2×EdU incubation working solution. Incubate for a certain period of time (the incubation time generally depends on the cell’s growth cycle and usually occupies about 10% of the cell cycle time. For most adherent cells with fast growth, incubate for approximately 2 hours. Adjust the incubation time based on cell characteristics, post-treatment conditions, etc. If a longer incubation time is needed, consider reducing the EdU working concentration; for a shorter time, consider increasing the EdU concentration).
2.3. After incubation, wash the EdU-labeled cell samples with PBS buffer 1-2 times, add the fixative solution, and cover the cells. Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes (for flow cytometry detection, if working with adherent cells, digest and resuspend the cells before fixation, then follow the processing methods for suspension cells). Wash 2-3 times with PBS buffer, each time for 3-5 minutes.
2.4. Remove the PBS buffer, add the permeabilization solution, and cover the cells or tissues. Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
2.5. Remove the permeabilization solution, wash with PBS buffer 1-2 times for 3-5 minutes each, then proceed to step 4.
- EdU injection for animal modeling and tissue section processing:
3.1. Perform EdU injections on animals according to experimental requirements, such as intraperitoneal injection, intramuscular injection, subcutaneous injection, tail vein injection, etc. The recommended dosage of EdU in relation to the animal’s body weight is 5 mg/kg. The specific injection amount depends on the research content and animal conditions. This kit provides a portion of EdU storage solution primarily for cell-based EdU labeling. If EdU modeling is required for animals, EdU reagent can be ordered separately (recommended G5059).
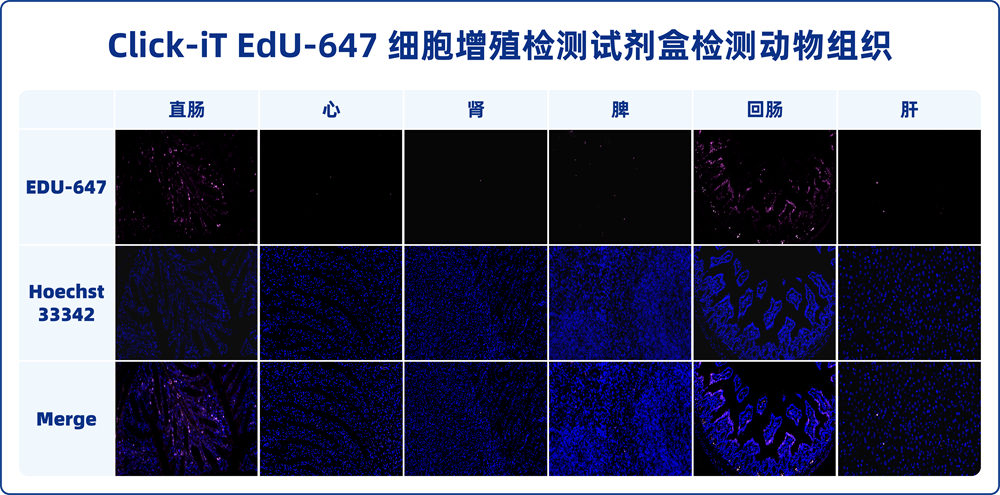
3.2. Tissues with fast cell proliferation rates, such as the small intestine, have shorter labeling times (less than 12 hours), while tissues with slower proliferation rates may require several days for labeling. The optimal labeling time depends on the specific experiment. Since the small intestine epithelial tissue has a fast proliferation rate, it is recommended as a reference for labeling time.
3.3. After euthanizing the animals according to the standard procedure, retrieve the desired tissues and prepare frozen sections or paraffin-embedded sections following standard protocols.
a. For frozen sections: Allow the sections to thaw at room temperature, add an appropriate amount of fixative solution, and fix at room temperature for 15 minutes. Remove the fixative solution, wash with an appropriate amount of PBS buffer 3 times, each time for 3-5 minutes. Remove the PBS buffer, add an appropriate amount of permeabilization solution, and incubate at room temperature for 10-15 minutes. Remove the permeabilization solution, wash with PBS buffer 1-2 times for 3-5 minutes each, then proceed to step 4.
b. For paraffin-embedded sections: Deparaffinize and rehydrate the sections, wash with PBS for 5 minutes. Remove the PBS buffer, add the permeabilization solution, and cover the cells or tissues. Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes. Remove the permeabilization solution, wash with PBS buffer 1-2 times for 3-5 minutes each, then proceed to step 4.
- EdU click reaction:
4.1. During the fixation and permeabilization of cells or tissues, prepare the click reaction mixture according to the specific sample system. The following table provides a reference protocol for 10 samples in a 96-well plate (100 μL per well). Adjust the amounts proportionally based on your specific needs. Add the components in the order listed in the table, and mix thoroughly while adding (prepare and use immediately).
For Cell Samples:
| Component | Volume |
|---|---|
| Reaction Buffer | 935 μL |
| Catalytic Agent (Reagent A) | 10 μL |
| Fluorescent Dye iF647 (Reagent B) | 5 μL |
| Catalytic Additive (Reagent C) | 50 μL |
| Total Volume | 1000 μL |
For Tissue Cell Sections:
| Component | Volume |
|---|---|
| Reaction Buffer | 928 μL |
| Catalytic Agent (Reagent A) | 10 μL |
| Fluorescent Dye iF647 (Reagent B) | 12 μL |
| Catalytic Additive (Reagent C) | 50 μL |
| Total Volume | 1000 μL |
For tissue cell sections, the reference system is used to prepare the click reaction mixture. Users can adjust the amounts proportionally based on the number of tissue samples, increasing or decreasing the volume, with approximately 100-200 μL of click reaction mixture needed to cover each tissue section sample.
4.2. Remove the PBS buffer from the previous step (Step 2.5 or 3.3) and add the click reaction mixture. Gently shake to ensure the reaction mixture covers all cells or tissues. Incubate at room temperature, avoiding light, for 30 minutes.
4.3. Remove the click reaction mixture and wash the cells or tissues with PBS buffer 2-3 times, for 3-5 minutes each time. (If no other specific requirements exist, you can use flow cytometry to measure the fluorescence intensity or use other instruments to assess the fluorescence effect.)
- Nuclear Staining:
5.1. Remove the PBS buffer from the previous step. Dilute the Hoechst 33342 staining solution with PBS buffer at a ratio of 1:500-1000, and add it to cover the cells. Incubate for 5 minutes.
5.2. Remove the Hoechst staining solution and wash the cells or tissues with PBS buffer 2-3 times, for 3-5 minutes each time.
- Imaging and Analysis:
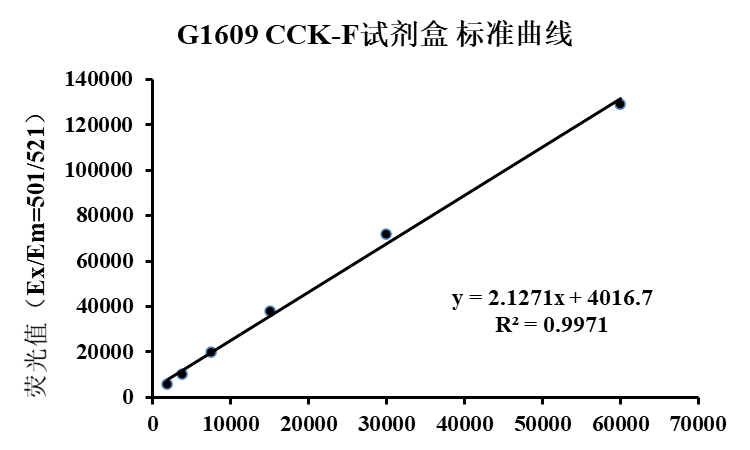
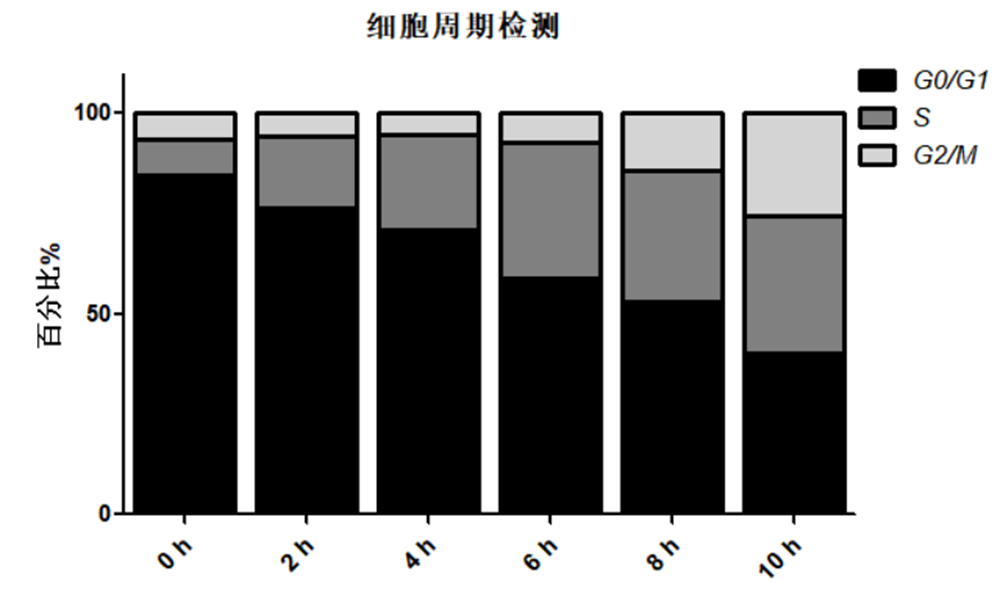
Directly place the cultured cells or tissue slice samples under a fluorescence microscope or confocal microscope for detection. Analyze the proportion of proliferating cells. Alternatively, collect the cultured cells and use flow cytometry to measure the fluorescence intensity (it is recommended to use non-labeled EdU cell samples as a negative control for flow cytometry and adjust the appropriate voltage). Based on the fluorescence intensity, determine the DNA replication activity during the S-phase of the cell cycle. The fluorescent dye iF647 (Reagent B) in this kit has spectral characteristics of Ex/Em: 656 nm/670 nm (pink), while the Hoechst 33342 staining solution has spectral characteristics of Ex/Em: 346 nm/460 nm (blue).
Note:
- For cultured cells, the specific concentration and incubation time of EdU can be adjusted according to the sample and research purpose.
- Some tissue cells have slow proliferation rates. To eliminate factors such as poor modeling effects, it is recommended to select tissue samples with rapid proliferation rates as reference samples (e.g., intestinal tissue).
- If the background color is too dark, it may be due to insufficient washing during the experiment, excessive fixation time of the tissue samples, or residual fixative.
- The catalytic additive (Reagent C) of EdU is prone to oxidation. It is recommended to avoid prolonged exposure to air. After preparing it as an aqueous solution, it is advisable to store it in aliquots. Based on testing, if the color of the catalytic additive changes slightly, the click reaction catalytic system can still function normally. If it turns brown, it indicates that the component has become ineffective and should be discarded.
- When performing the procedure, please wear a lab coat and disposable gloves.
This product is for research use only and is not intended for clinical diagnosis.
Version: V1.0-20210