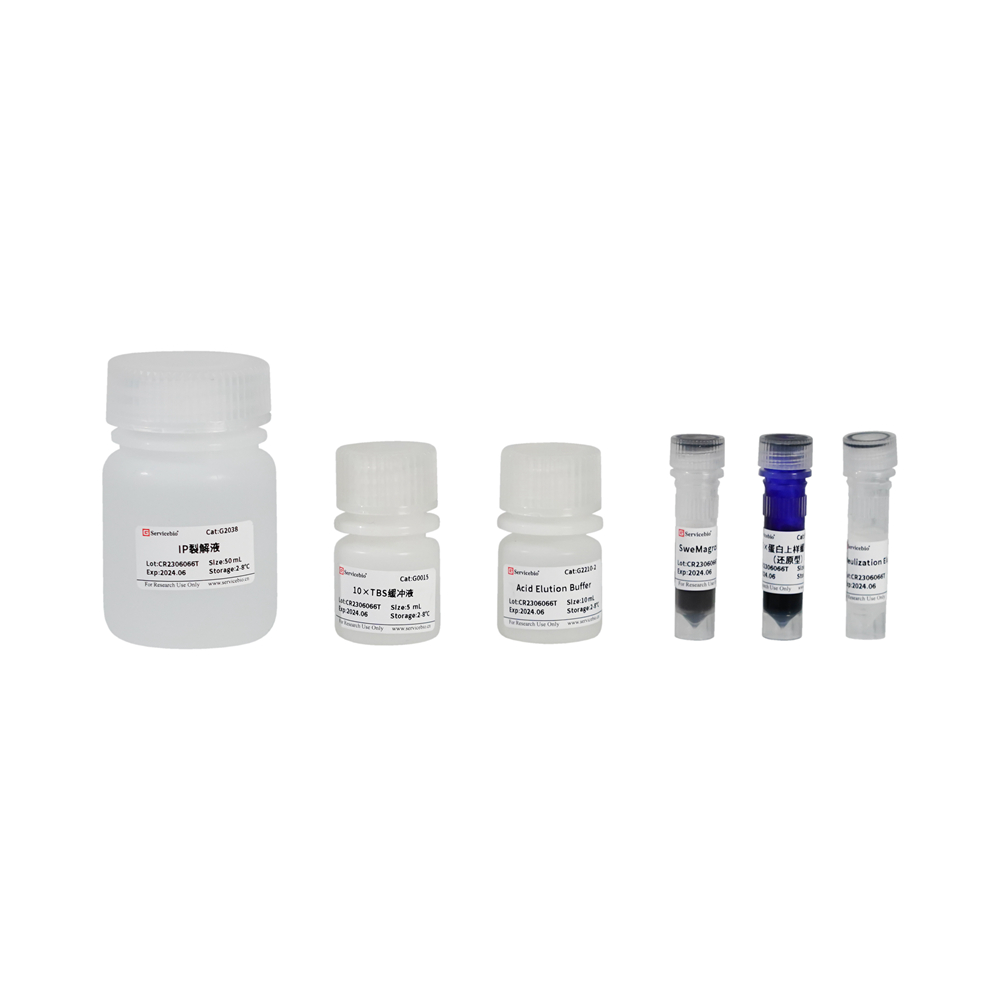
Description
Product Information
- Product Name: Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit (Protein G Magnetic Bead-Based)
- Product Number: G2210-50T
- Specification: 50T
Product Introduction
Immunoprecipitation or co-immunoprecipitation is a common technique used to study protein-protein interactions (PPIs). It involves the use of specific antibodies and media that can bind to antibodies, such as Protein A/G Agarose or Protein A/G Magrose, or directly using media coupled with specific antibodies, such as agarose gel or magnetic beads. This technique allows the separation of antigen-antibody complexes from a solution through centrifugation or magnetic forces, thereby facilitating the isolation and purification of the target protein. The purified protein can then be used for protein immunoblotting (Western Blot) or mass spectrometry analysis.
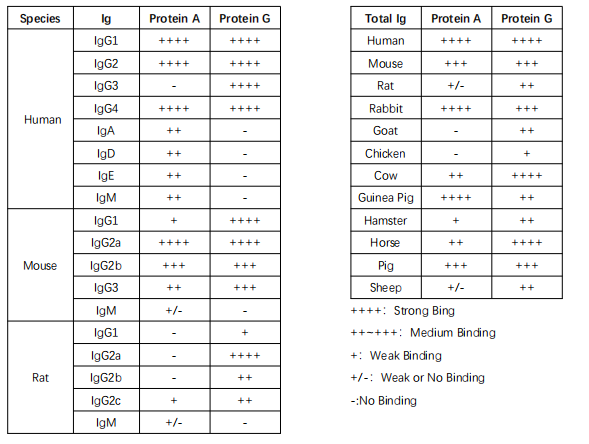
Protein A is a cell wall surface protein found in Staphylococcus aureus with a molecular weight of 42 kDa, while Protein G is an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed by C-type or G-type streptococcal bacteria. Both Protein A and Protein G can specifically bind to mammalian immunoglobulins (Ig). Recombinant Protein A and G, when coupled with magnetic beads in a specific manner, can be used for immunoprecipitation or antibody purification.
Protein A beads are suitable for immunoprecipitating human IgG1, IgG2, IgG4, mouse IgG2a, IgGb, and more, while Protein G beads are suitable for immunoprecipitating human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, mouse IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, rat IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG2c, as well as various monoclonal antibodies (see specific information in Table 1).
This product uses self-developed Protein G protein-labeled magnetic beads, which, compared to similar products on the market, have higher antibody binding efficiency and lower non-specific binding rates. When used with optimized buffers, this product allows for convenient and efficient immunoprecipitation experiments. It can be widely applied to the separation and purification of target proteins from cell lysates, cell culture supernatants, serum, ascites, and other samples. The kit provides two elution methods (denaturing elution and acid elution) for the elution of target proteins. In particular, acid elution does not contain antibody light chains and heavy chains, effectively addressing interference issues with antibody heavy and light chains in protein immunoblotting experiments after immunoprecipitation.
For your reference, the English translation of the product information is as follows:
Product Information
- Product Name: Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit (Protein G Magnetic Bead-Based)
- Product Number: G2210-50T
- Specification: 50T
Product Introduction
Immunoprecipitation or co-immunoprecipitation is a common technique used to study protein-protein interactions (PPIs). It involves the use of specific antibodies and media that can bind to antibodies, such as Protein A/G Agarose or Protein A/G Magrose, or directly using media coupled with specific antibodies, such as agarose gel or magnetic beads. This technique allows the separation of antigen-antibody complexes from a solution through centrifugation or magnetic forces, thereby facilitating the isolation and purification of the target protein. The purified protein can then be used for protein immunoblotting (Western Blot) or mass spectrometry analysis.
Protein A is a cell wall surface protein found in Staphylococcus aureus with a molecular weight of 42 kDa, while Protein G is an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed by C-type or G-type streptococcal bacteria. Both Protein A and Protein G can specifically bind to mammalian immunoglobulins (Ig). Recombinant Protein A and G, when coupled with magnetic beads in a specific manner, can be used for immunoprecipitation or antibody purification.
Protein A beads are suitable for immunoprecipitating human IgG1, IgG2, IgG4, mouse IgG2a, IgGb, and more, while Protein G beads are suitable for immunoprecipitating human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, mouse IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, rat IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG2c, as well as various monoclonal antibodies (see specific information in Table 1).
This product uses self-developed Protein G protein-labeled magnetic beads, which, compared to similar products on the market, have higher antibody binding efficiency and lower non-specific binding rates. When used with optimized buffers, this product allows for convenient and efficient immunoprecipitation experiments. It can be widely applied to the separation and purification of target proteins from cell lysates, cell culture supernatants, serum, ascites, and other samples. The kit provides two elution methods (denaturing elution and acid elution) for the elution of target proteins. In particular, acid elution does not contain antibody light chains and heavy chains, effectively addressing interference issues with antibody heavy and light chains in protein immunoblotting experiments after immunoprecipitation.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Content | 50 mg/ml magnetic beads stored in special buffer |
| Magnetic Type | Superparamagnetic |
| Coupling Protein | Protein G |
| Coupling Protein Molecular Wt | ~25 kDa (Protein G) |
| Binding Capacity | >1 mg of mouse antibody per ml of beads |
| Specificity | Antibodies from various species, including mouse, human, rat, goat, sheep, and cow |
| Bead Size | 30~150 μm |
| Elution Methods | Acid elution or 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) elution |
| Note | When using 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) elution, heavy chains (~50 kDa) and light chains (~25 kDa) of antibodies are denatured and released from the beads |
| Applications | Protein immunoprecipitation, co-immunoprecipitation, protein purification and isolation |
| Storage and Transportation | Shipped on wet ice; store 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) at -20℃, other components at 2-8℃, with a shelf life of 12 months |
Reagent Kit Components:
| Component Number | Component | Cat. Number | Storage Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| G2209-50T | IP Lysis Buffer | G2038 | 2-8°C |
| G0015 | 10× TBS Buffer | 2-8°C | |
| G2209-1 | SweMagrose Protein G | 2-8°C | |
| G2209-2 | Acid Elution Buffer | 2-8°C | |
| G2209-3 | Neutralization Elution Buffer | 2-8°C | |
| G2013 | 5× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) | -20°C | |
| User Manual |
Required Reagents:
| Product Name | Cat. Number | Spec. |
|---|---|---|
| 50× Cocktail蛋白酶抑制剂 | G2006-250UL | 250 μL |
| PBS, 1× (Phosphate Buffered Saline) | G4202-500ML | 500 mL |
Operational Steps:
Step 1: Preparation of Reagents
a) Refer to the table below to prepare the relevant reagents based on the ratio of 100-500 μL of lysis buffer for each sample.
| Step | Required Solution | Volume for One Sample | Volume for Multiple Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP Lysis Buffer (with Cocktail Protease Inhibitor) | 100 μL | 500 μL | |
| SweMagrose Protein G | 4 μL | 20 μL | |
| 10× TBS Buffer | 100 μL | 500 μL | |
| Acid Elution Buffer | 20 μL | 100 μL | |
| Neutralization Elution Buffer | 20 μL | 100 μL | |
| 5× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) | 20 μL | 100 μL |
Please note that this table provides an overview of the reagents and volumes required for each step. You may need to adjust the volumes based on the number of samples you are processing.
Step 1: Preparation of Reagents
a) Preparation of IP Lysis Buffer with Protease Inhibitor Cocktail: Dilute IP Lysis Buffer (G2038) with 50× Cocktail Protease Inhibitor (G2006-250UL) in a 50:1 ratio. For example, add 20 μL of 50× Cocktail Protease Inhibitor to 1 mL of IP Lysis Buffer. Prepare this solution freshly and keep it on ice or at 4°C.
c) Note: If your target protein for immunoprecipitation is phosphorylated or acetylated, you may need to add phosphatase inhibitors or deacetylase inhibitors (not provided). It’s recommended to prepare the inhibitor-containing IP Lysis Buffer immediately before use and not store it for later use.
d) Preparation of 1× TBS Buffer: Dilute 10× TBS Buffer with ultrapure water to achieve a 1× concentration. For example, add 1 mL of 10× TBS Buffer to 9 mL of ultrapure water and mix well to obtain 1× TBS Buffer.
e) Preparation of 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing): Dilute 5× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) with ultrapure water at a 5:1 ratio to obtain a 1× concentration. For example, add 0.2 mL of 5× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) to 0.8 mL of ultrapure water and mix well to obtain 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing).
Step 2: Sample Preparation
After cell lysis, immediately proceed with immunoprecipitation (IP) or immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiments. If you cannot proceed immediately, you can store samples at -20°C or -80°C, but be aware that freeze-thaw cycles may affect protein-protein interactions. Perform all sample preparation steps on ice or at 4°C to minimize protein degradation.
For Tissue Samples: a) Wash the tissue with pre-chilled PBS (recommended G4202) to remove blood contaminants. Cut the tissue into small pieces and place them in a homogenizer.
b) Add IP Lysis Buffer with Cocktail Protease Inhibitor to the tissue in a 100-200 μL ratio per 10-20 mg of tissue (adjust the volume for higher protein concentrations if needed).
c) Homogenize the tissue using a glass homogenizer or a handheld homogenizer. Alternatively, use the KZ-III-F low-temperature grinder developed by our company.
d) Transfer the homogenate to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, vortex and incubate on ice for 30 minutes, with periodic pipetting every 10 minutes to ensure complete cell lysis.
e) Centrifuge at 12,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant, which contains total protein. This can be used for subsequent immunoprecipitation or Co-IP experiments.
For Adherent Cell Samples: a) If necessary, wash the cells 2-3 times with PBS. Remove the final wash thoroughly.
b) Scrape the cells or trypsinize and collect them in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes and discard the supernatant to obtain the cell pellet.
c) Add IP Lysis Buffer with Cocktail Protease Inhibitor in a 100-200 μL ratio per 50-100 million cells. Gently tap the tube or pipette up and down to ensure thorough cell lysis. If you have a larger number of cells, it’s recommended to divide them into aliquots of 50-100 million cells per tube for better lysis.
d) Incubate the cell lysate on ice for 3-5 minutes, ensuring complete cell lysis without significant cell pellet formation.
e) Centrifuge at 12,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant, which contains total protein and can be used for subsequent immunoprecipitation or Co-IP experiments.
For Suspension Cell Samples: a) Centrifuge the cells at 1,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes to collect the cell pellet. If necessary, wash the cells once with PBS, then remove and carefully aspirate the residual liquid.
b) Add IP Lysis Buffer with Cocktail Protease Inhibitor in a 100-200 μL ratio per 50-100 million cells. Gently pipette to ensure thorough cell dispersion. If you have a larger number of cells, it’s recommended to divide them into aliquots of 50-100 million cells per tube for better lysis.
c) Incubate on ice for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes. Collect the supernatant, which contains total protein, and use it for subsequent immunoprecipitation or Co-IP experiments.
For Bacterial or Yeast Samples: a) Take 1 mL of bacterial or yeast culture, centrifuge, and remove the supernatant. If necessary, wash once with PBS and remove any remaining liquid.
b) Add IP Lysis Buffer with Cocktail Protease Inhibitor in a 100-200 μL ratio.
c) Incubate on ice for 10 minutes. If better lysis is needed, consider using lysozyme and zymolyase (not provided) for bacterial and yeast samples, respectively, before using IP Lysis Buffer for lysis.
d) Centrifuge at 12,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant, which contains total protein and can be used for subsequent immunoprecipitation or Co-IP experiments.
Step 3: Magnetic Bead Preparation
a) Gently resuspend the SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads to create a uniform suspension. Add 20 μL of the mixed and evenly resuspended bead suspension to each sample as per the typical example of adding 20 μL of bead suspension for each 500 μL sample.
b) Gently resuspend the beads, place them on a magnetic separation rack, and allow them to stand for 30 seconds to attract the beads. Carefully remove the supernatant, and repeat this step two more times.
c) Resuspend the beads in 1× TBS to the original volume as prepared initially.
Step 4: Binding of Antibody to SweMagrose Protein G Magnetic Beads
a) Prepare the antibody by diluting it in 1× TBS following the recommended dilution ratio in the antibody usage instructions or at a final concentration of 5-50 μg/mL. Keep the antibody solution on ice.
b) Add the antibody solution (or normal IgG as a control) to the previously prepared SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads. Incubate this mixture at room temperature with gentle rotation for 15-60 minutes.
c) Wash the beads: After incubation, use a magnetic separation rack to attract the beads. Carefully remove the supernatant, and add 500 μL of 1× TBS. Gently pipette to resuspend the SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads. Place the tubes on the magnetic separation rack for 10 seconds to separate the beads. Remove the supernatant and repeat the washing process three times. After each wash, resuspend the beads in 1× TBS to the initial volume.
Step 5: Immunoprecipitation (IP)
a) Optionally, remove non-specific binding: For control experiments, you can use the SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads pre-bound with normal IgG (from Step 4) to capture non-specific proteins. Incubate the beads with the sample for 60 minutes at 4°C, then separate the beads and collect the supernatant for subsequent experiments. This step helps remove proteins that bind non-specifically to normal IgG.
b) Sample incubation with SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads: Add the sample to the SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads that were pre-bound with antibody or normal IgG. Use a ratio of 20 μL of bead suspension for each 500 μL of protein sample. Place the tubes on a shaker or rotating mixer and incubate for 2 hours at room temperature or overnight at 4°C.
c) Magnetic separation: After incubation, use a magnetic separation rack to attract the beads. Carefully remove the supernatant.
d) Wash the beads: Add 500 μL of 1× TBS, gently pipette to resuspend the SweMagrose Protein G magnetic beads, and place the tubes on the magnetic separation rack for 10 seconds to separate the beads. Remove the supernatant and repeat the washing process three times. After each wash, resuspend the beads in 1× TBS to the initial volume.
Step 6: Elution
You can choose one of the following methods for elution based on the properties of your target protein and the requirements of your subsequent experiments:
Denaturing Elution: Suitable for SDS-PAGE analysis. Remove the EP tube containing beads from the magnetic separator. Add 25 μL of 1× Protein Sample Buffer (Reducing) to the beads, mix well, and heat at 95°C for 5 minutes. Then perform magnetic separation to collect the eluate for Western blot analysis.
Acid Elution: Suitable for preserving the biological activity of your target protein. Remove the EP tube containing beads from the magnetic separator. Add 20 μL of Acid Elution Buffer, mix well, and incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes. Then perform magnetic separation and collect the eluate in a new EP tube. Immediately add 2 μL of Neutralization Elution Buffer to adjust the pH of the eluate to neutral. This eluate can be used for subsequent functional assays.
Note: Adjust the volumes of elution buffer as needed based on your experimental requirements.
Additional Notes:
- Do not store SweMagrose Protein G components at -20°C or subject them to repeated freeze-thaw cycles as it may affect bead performance and introduce experimental errors.
- Read the operating instructions carefully before conducting immunoprecipitation experiments.
- You will need to provide a magnetic separation rack for magnetic bead separation.
- If your immunoprecipitation targets phosphorylated or acetylated proteins, you will need to provide the appropriate phosphatase inhibitors and deacetylase inhibitors.
- Maintain the pH of the magnetic beads between 6-8, avoid high-speed centrifugation, drying, or freezing, and do not leave the beads in a magnetic field for an extended period, as it may cause bead aggregation.
- Thoroughly mix the magnetic beads before use. Mixing should be gentle and avoid vigorous vortexing or shaking to prevent antibody denaturation.
- For immunoprecipitation, it is recommended to include positive and negative control groups (SweMagrose Mouse IgG).
- After collecting protein samples, complete the purification work as soon as possible and keep them at 4°C or on ice to slow down protein degradation or denaturation.
- During acid elution, bead aggregation may occur. This is normal and does not affect bead performance.
- This product is for scientific research use only and should not be used for clinical diagnosis or treatment, food, or drug purposes. Do not store it in regular residential areas.
- For your safety and health, wear lab attire and disposable gloves during the operation.
- Protein A and Protein G have varying binding capacities for antibodies from different species and subtypes. Refer to Table 1 for details on the binding capacity.